All of us are aware of ever-increasing competition and commoditization in the world of consumer electronics. Due to which companies are finding it difficult than ever to differentiate their products in the market. Price sensitivity of consumers is also forcing companies to become highly cost conscious. Apart from being energy hungry consumer electronic equipment are also characterized by short product life cycle and difficult to repair. According to the department of Electronics and Information Technology (DeitY), India, the production of electronic products in 2013 has increased by 110% as compared to production in year 2008 [1]. Electronics items contain several rare earth, heavy metals and toxic metals such as terbium, lead, mercury, cadmium etc. and with increase in demand of consumer electronic products; there is an increasing impact on environment and well being of society. Once electronic items reaches end of their useful life most of them find way to regular garbage bin, which eventually piles up as a landfill. Only minuscule quality of the e-waste reaches certified recycling facilities.
As with every challenge there is an opportunity, so is in this situation as well. Consumer electronics companies can develop effective green supply chain to differentiate products in overcrowded market and reduce cost over a period of time to gain sustainable competitive edge. Green supply chain should stretch from supplier’s supplier to customer’s customer. It starts with product conceptualization phase and does not have any absolute end, as it becomes a cyclic process. Companies can undertake following steps to incorporate green supply chain in their business model:
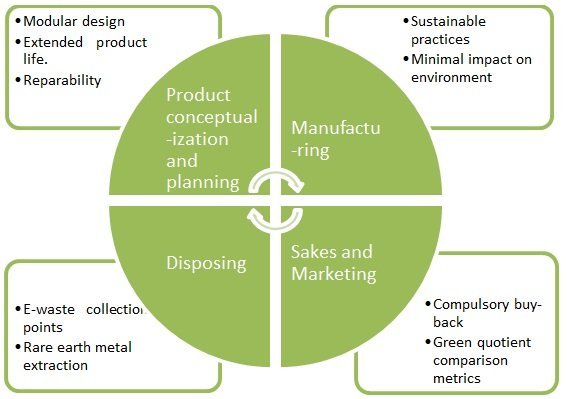
Figure 1: Sustainable supply chain model for electronic products
- Product conceptualization and design phase
Companies should design their product for durability and elongated useful life. Modular design of the product should be encouraged so as to make the products easy for repair, reuse and decompose. Electronic product should be designed considering future upgrades and expansions. Common point of failure of product should be analyzed and product should be design for easy replacement of those parts. Product design planning should have a minimal useful life as one of the design criteria.
- Manufacturing
During manufacturing stage companies should follow sustainable manufacturing practices, to certain extend companies should internalize overall negative externalities generated during manufacturing of electronics products.
- Sales and Marketing
While selling and marketing consumer electronic products, consumers should be made aware of the process initiated by the company to increase the useful life of the product, repair and upgrade, which is definite improvement in customer value proposition. Also at the time of sales users should be made aware of compulsory buy-back and safe disposal programs.
Apart from popular comparison based on product feature and prices, the NGO’s, Consumer groups or government should devise easy to use method to compare the green quotient of electronic products from different manufacturer. This will reinforce steps taken by the company in the entire supply chain for making their product environmental friendly.
- End of useful life
Government of India has constituted a law for e-waste (Management and Handling) Rules 2010 which came into effect on May 1, 2012. As per law responsibility of the manufactures are extended to cover end-to-end life cycle of the product under ‘Extended Producer Responsibility (ERP) clause and manufacturer are encouraged to work towards Reduction of Harmful Substances (RoHS) in their products.
Once the product reaches end of its useful life, as per government regulation, the product should be transferred back to the manufacturer. However there is a high transaction cost involved in this process as points of disposing products are not as visible and approachable as point of sell. And many companies are asking consumer to call upon registered dismantlers to dispose of the units. These limitations make the entire ERP clause ineffective. However manufacturer can work towards eliminating this disparity by having healthy ratio of points of e-waste collection and points of sale in a region. Electronic equipment manufacturers can join hands to form an aggregator for waste collection and safe disposal to bring down the cost.
As we have seen there are multiple opportunities for electronic equipment manufacturers to turn towards green supply chain. Investment made towards green efforts might take some time to yield results in financial terms however in near term green efforts will help manufacturers to create a positive brand image and differentiate. Green supply chain have a considerable impact on the buying decisions of millennial, a major consumer segments of electronic gadgets, in developing countries as per the research conducted by Nielsen [3]. Over the period of time availability of natural raw material such as rare earth metals are going to become more scarce, manufacturers who can develop the competency in managing and effectively reusing such scantly available natural resources can gain significant competitive advantage in long term both technologically and cost wise. Clue of financial viability of recycle and reuse business model can be taken from Attero; a Noida based e-waste management company, which has attracted an investment from PE investors [4].
Diran Apelian, founding director of the Metal Processing Institute in Worcester, Massachusetts said “There’s something like 32 tons of gold in all the world’s cell phones, there’s a huge goldmine in our urban landfills.”[2]
Green supply chain improves the supply chain quality starting from the procurement to the disposal have minimal negative impact on the environment. Currently manufacturer’s primary motto is to maximize their profitability and their dominant logic indicates that environment friendly products will reduce profit margins. Although adopting environmental friendly activities might not result in short term gain but will eventually reflects its advantages in company’s bottom line in long term. Adopting such practices early can help the company sustain in future when there will be severe resource crunch and such practices will become necessary for the survival.
Reference:
[1]http://data.gov.in/catalog/electronics-and-it-production#web_catalog_tabs_block_10
[2]http://e360.yale.edu/feature/a_scarcity_of_rare_metals_is_hindering_green_technologies/2711/
[3]http://www.nielsen.com/us/en/press-room/2014/global-consumers-are-willing-to-put-their-money-where-their-heart-is.html
[4] http://qz.com/149632/the-indian-company-turning-e-waste-into-mounds-of-profit/
[The article has been written by Neha Bajaj and Ashutosh Maheshwari]
Tags: e-waste environment Green supply chainYou might like reading:

What does Indian Budget 2013-14 mean for the Common Man?
As Mr. Swaminathan Aiyar has rightly put it, never before has a Finance Minister rejected populist giveaways so decisively in an election year, as Mr. P Chidambaram has done in the last Union Budget before the 2014 General Elections. What this means is that the FM has sought a different strategy, by accelerating GDP growth & reducing the fiscal deficit, […]

WhatsApp, WeChat, LINE – Revolutionary communication apps !
Let me run the time machine in reverse direction to second half of 2000s i.e. 2006-2008, when the so called Short Messaging Service known as SMS was still the most preferred type of communication amongst all classes. Be it enquiring from a friend whether a professor has started his melodious lullaby or not, or asking someone to call you back […]