India and Bharat, the two geographies or mentalities view each other with suspicion. For India, Bharat is about ‘khap-panchayats’ that kill daughters that dare stand up against the family pressure. For Bharat, India is where ‘homosexuality is acceptable’. For India, Bharat is where minorities are massacred. For Bharat, India is where traditions are not respected. For India, Bharat is the land of Hindu fundamentalists. For Bharat, India is the land of loose moral values. For India, Bharat is where bullock carts crawling roads are muddy. For Bharat, India is where sports cars are enjoying roller-coaster on tar roads with potholes.
For India, Bharat is where you do not get 3G network, for Bharat, India is where everyone is boasting off their upcoming 4G enabled devices. We are not here to discuss the roots of having two mentalities India and Bharat but to explore the opportunities in the digital gap between these two geographies/mentalities.
With 100 different cities from Tier1, Tier2 sectors from both Bharat and India, coming forward to become SMART, India is trying to address one of the biggest obstacle it is facing today in becoming a Super Power; “Digital Divide”. The ability to create and utilize information plays a significant role in both socioeconomic structures of our lives. The digital divide can be defined as the gap between individuals, households, business and geographical areas at different socio-economic levels with regards both to their opportunities to access ICTs(Information Communication Technology) and to their use of the internet for a wide variety of activities. As internet has rapidly grown to underline almost all aspect of the global economy, the term “Digital divide” has often been referred to internet access. It is a divide that affects and reinforces fundamental economic and social divides between and within countries and is threatening to further exacerbate these inequalities.(Singh.k, 2012)
The term “digital divide”, is said to have been coined a decade ago, by a former United States Assistant secretary for commerce for telecommunications and communication, Larry Irving. Jr, to focus attention on the existing gap in access to information services between those who can afford to purchase the computer hardware and software necessary to participate in the global information network, and low income families and communication that cannot help reach out to masses.(Dragulanescu, 2002).
The eight success factors in the internet economy formulated by Rao (2000) provide a classification that is strongly oriented to technological and economic dimensions such as-
Connectivity, Capacity, Content, Community, Capital, Policy framework, National information policies, IT, knowledge society, e-government, technology transfer, rural transfer, etc. Moral and ethical framework.
A digitally divided India : A digital divide in India can look very easy to define but it is more than what meets the eye. We may define the digital divide by distinguishing between the rich , powerful who are technologically connected and live in the Information Age and one who are poor and powerless struggling to satisfy the basic needs of life. Although this is true to some extent , we cannot define this as a divide. India cannot be divided only on the basis of these parameters but also only the basis of language, culture ,education , locality etc.According to TRAI, the internet connection in India reached to 164 million out of a population of 1.28 billion .According to Internet and Mobile Association of India (IAMAI) and consultancy firm KPMG , India , at present has 159 million Internet users , which are going to double (314 million) by 2017. Out of the these users 71% of internet users are urban . There are the rich , English speaking minority amongst the population of 1.28 billion. There is no doubt that there is digital divide in India based on income .
A major reason for the digital divide in India ,apart from income , is language and culture. In India, only 10% of the population speaks English, whereas the others speak vernacular languages. The fact cannot be ignored that around 60-80% of websites in the world are in English. Thus language becomes a major barrier for remaining 90% of the Indians to uncover the knowledge that the internet holds.
Another reason for the digital divide in India is low literacy rate. As per Population Census of India 2011, the Literacy rate of India is 74.04% .On a positive note , it has shown increase of 9 percent in the last 10 years. But even with the improvement , the literacy rate is still a reason for digital divide in India since only 10% of the population knows English. For Indians who speak no English the barriers to information age are inseparable. Thus in practice unless Indian know English which most Indians do not, no matter how be computer use and internet access are effectively.
The education system in India could also be one of the reasons for the digital divide. The Indian education system does not inculcate the use of information technology at schools .If information technology is introduced to students right from the school level not only will be students come to know about various strategies of searching the net but also their learning will increases to a significant level.
Also, One cannot ignore the lack of infrastructure for enabling Information technology in the country. India has a very low penetration of Internet which stands at 19.9 %.Some of the reasons for impediments in developing this infrastructure were government policies with respect to telecom, investment in laying optical fibres etc.
Lastly, before the Modi Government there was also a lack of understanding the importance of information technology and lack of vision about bridging the this digital gap. Thankfully, that seems to be changing with the Modi Government coming into power.
Bridging the Digital Divide : Various initiatives are being introduced by the government as well as the corporate to bridge the digital divide in the country. The prime Minister seems to be clear in his vision , of making the country Digital by introducing programs like ‘Digital India ‘ with a focus on rural India. Digital India plan , which is an umbrella initiative has an initial outlay of Rs 1.13 lakh crores. It covers 9 programs including electronic manufacturing, e-Kranti (electronic delivery of services) and achieving 100% mobile density by 2018. Digital India, basically bases itself on three pillars utility, government service delivery and digital empowerment of people . The government has planned to execute 31 e-government projects out of which 21 are already operational. These enable 90 lakh transactions a day changing the lives of around 30 crore people. In addition to these initiatives, the government is also improving the infrastructure of the nation. Construction on India’s multibillion dollar high speed broadband network which will connect 600 million rural citizens has begun. The government accepts that the biggest challenge for India to go Digital is the lack of digital literacy , it , thus , envisions of make at least one family member digitally literate by establishing training centres all over the country. The corporate are also participating actively in all this action. India Inc. has pledged to invest 4.5 lakh crore ‘Digital India’. The Tatas, Birlas are hugely investing in the telecom sector , manufacturing etc. Companies like Facebook and Google are coming with initiatives like drones and balloons for internet access. Surely, the digital gap is going to narrow in the coming future.
After considering the challenges to bridge the digital divide in India , it can be said that their is a need for the creation of a collaborative environment , innovation . There is a need to develop a digital workforce, strong entrepreneurial support system, creation of ecosystem for online shift ,providing key infrastructure and services. Information Technology has the power to assist people to satisfy their basic needs no matter what rank or place in the society. A digitally empowered India can change the lives its 1.28 billion people. It won’t be long for this young nation to be a world superpower because of digitalisation. The government , corporate and importantly the citizens understand this. It is a positive sign that Digital Divide in India is getting attention not only from the government but also from India Inc and steps are being taken to bridge the gap.
[The article has been written by Vinay Mahadik and Parija Pradhan.]
Tags: Digital Divide India Information technologyYou might like reading:
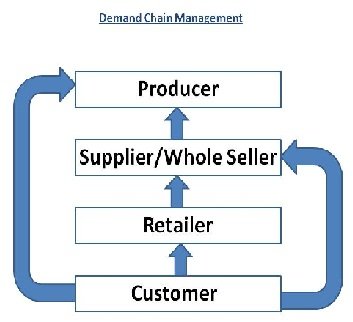
Demand chain Management – A new era Business Model
Supply Chain Management (SCM) is an old fascinated marketing funda for Retail Business. Demand Chain Management (DCM) – is not something abstract. It is the real business strategy by new era business leaders. From Dell Computer to FilpCart, many new companies follow demand chain management principle. In a simple word DCM is “If customer demands then only supply” In the […]

Deciding the right equity stocks for your portfolio
Equity as an asset class is known to give the highest returns among other asset classes such as bonds and derivatives. In fact, it can be considered as an inflation hedge as if the price of commodities increase it will be matched with higher sales thereby implying significantly higher cash flows. Equity investments also provide one the benefits of capital […]