The global financial slowdown has posed a major concern on the economic growth & prospects of future. So policy makers are framing many short term and long-term financial policies to stabilise the economic situations and bring back the growth trajectory. Schumpeter (1911) believes that proper financial planning is the key driver of future economic growth because efficient financial investments would milk better returns which can be invested to development work. Further, Robinson (1952) stated that economic status is the key driver to financial investments across different segments according to the requirement of funds. Lucas (1988), rejected Robinson’s proposal and said finance is a more complex entity and it channels the investments in different portfolio deciding the economic prospects/ growth of a nation. However the causality is still not yet clearly established but it is clear from many instances that these two factors are strongly positively correlated from the fact that better performing financial markets are economically better off.
This relationship has resulted in various financial policy changes like deregulation of tax policies, ease of doing business in developing nations to promote financial development which will have its influence in the long-term economic development/growth of the nation. For instance, India has realised that it is facing the following issues:
- Financial deficit is high
- Unemployment rate is high
- Black money is high in the economy
- Doing Business in India is becoming increasingly difficult because of different levels of clearances at different levels
- Increasing dependence on imports.
So to handle this, government has the following plan for the budget 2015:
- Reduce corporate tax from 30% to 25% over the next 4 years so as to encourage doing business in India and bringing measures by eliminating multiple clearances to set up business in India.
- Promote manufacturing in India by reducing import duty on high end intermediate goods required for assembling electronic equipments like fridge, microwave oven and increasing emphasis on infrastructure to improve connectivity and thus reducing the overall cost.
- Increasing the threshold on non-taxable income to 3,00,000 lack per annum and increase the slab on minimum tax payment slab from 3,00,000 to 5,00,000 to 3-10 lack and abolish the wealth tax on super rich people (income > 1Cr) and increase income tax from 30% to 32%. This is done so that middle and lower income class will be left with more purchasing power and charge more from richer class who has high spending power.
- Increase the slab on savings under 80C from 1 lack to 1.5 lack and promote pension scheme by including it under 80CC clause and provide tax benefit upto savings of 50,000 rupees annually.
- To have a better control on black money, government increasing indirect tax so that all consuming people have to pay tax upon suing goods and services.
If observed closely, it is evident that the government is following contraction budget policy because it wants to restrict liquidity and have a better control on inflation in India which is one of the major concerns. Economic status of the nation is not measured by mere average per capita income rather; equality in earning and purchasing power parity has to be considered. This is the reason government has modified its tax policy so that poor and middle class people would have higher purchasing power and government getting better financial inputs by making suitable changes in indirect tax because it is applicable to all and hence having a better control on black money.
Financial development & Economic growth – linkage
An efficient financial system facilitates efficient trade of goods and services by reducing cost on information and transaction costs.
India:
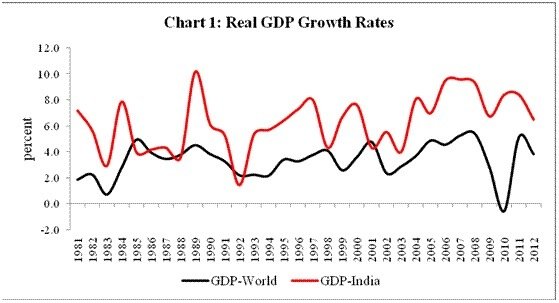
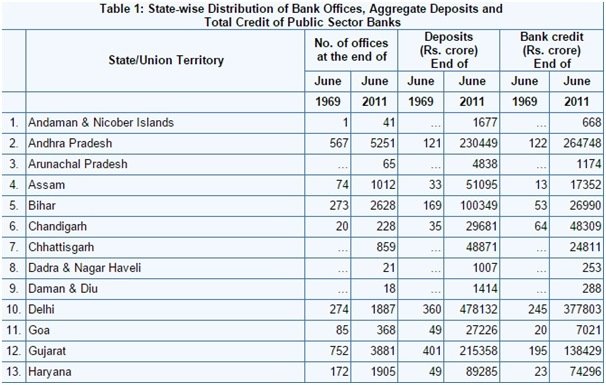
- As observed from table 1 & 2 in appendix, the % credit provided by bank as a percentage of GDP has increased subsequently over the period whose influence on GDP growth is well evident. Further it is attributed to freeing of economic reforms and making it easy for private players to do business. Further, the gap between the global GDP and domestic GDP has widened towards the later period because of reforms brought by the government to promote FDI in various sectors.
- From table 2 & 3, it is observed that the government has eased credit policy and hence the private credit had increased over the period and this has a positive correlation with the increased GDP growth above the global average.
- From table 4, it is observed that Market capitalization as a ratio of GDP has fallen sharply in 2008 and has rebound back. This was the period of global financial market crisis. This clearly shows that positive correlation existing between financial development & economic growth.
- From table 3 & 4, it is clear that as the number of banks is increasing (penetration), there is a correspondent increase in credit availability for the people which inturn is having a positive influence on the increase in market capitalization percentage.
- From table 1 & 4, it is observed that % credit provided by bank as a percentage of GDP has increased over the period. Subsequent to that there is an increase in market capitalization as a percentage of GDP. This clearly indicates a positive correlation existing between the private credits and the economic growth.
China:
- China had changed its economic policy in 1978 and opened its door for FDI and its per capita GDP has increased from less than $150 to $ 8,227 in 2012 (Table 5).
- Further the above growth is also ascertained to increasing financing of manufacturing industries (85 of Fortune 500 companies are located in China) and excessive investments on infrastructure to promote trades(This is very evident from the fact that the coastal region of China is prosperous and has superior infrastructure and is trading hub. However middle portion of China is suffering from poverty.)
Brazil:
Brazil’s growth strategy is ascertained to more investment on modernization of agriculture which is having a positive influence on GDP growth and a consistent inflation.
Inference:
It is very well evident that there exist a positive correlation between the financial development and economic growth. However not all financial investments would lead to economic development. Also for a financial policy to reflect its effect on the economic development, sufficient time has to be given. Also other macroeconomic parameters have to be considered to ascertain the efficiency / effectiveness of the financial policies.
Appendix:
Table: 1
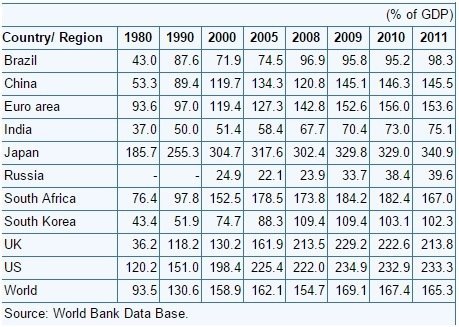
Domestic credit provided by bank as a % of GDP
Table: 2
Source: RBI website
Table: 3
Source: RBI website
Table: 4
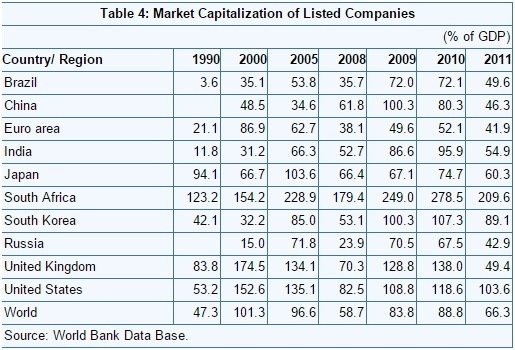
Table: 5
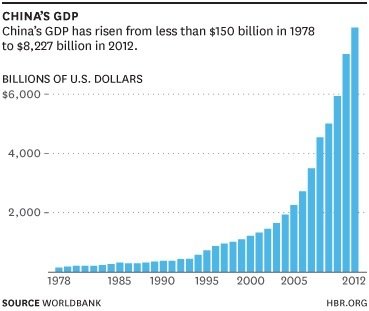
Table: 6
References:
- International Journal of Economic Practices and Theories, Vol. 3, No. 3, 2013 (July), e-ISSN 2247–7225
- http://www.rbi.org.in/scripts/PublicationsView.aspx?id=14945
- https://hbr.org/2013/11/chinas-economy-in-six-charts/
You might like reading:
IIM Calcutta Placements 2016 : 100% Placements in 2.5 days
IIM Calcutta achieved 100% final placements for the Class of 2014-16 in just 2.5 days. IIM Calcutta saw great enthusiasm from the industry to recruit some of the brightest minds of the country. For the largest batch of 439 students amongst the older IIMs, a whopping total of almost 500 offers were made during the entire process, including 21 international […]

How I cracked IIFT ? Unlocking the secrets…
Centre: IIFT Kolkata, 1st slot 9:30 am. Date: 03/02/2014 Written Score: 56.73 Cutoff: 48.xx Background: 10th: 91% ICSE 12th: 84% ICSE Grad: 80.7% (B.Tech Computer Science & Engineering) Work-ex: 36 Months (Infosys Limited) The first call of the season and IIFT it was. After a forgettable CAT result, IIFT was the one top notch college which I badly needed to […]