Foreign Exchange Market
The Indian foreign exchange market has witnessed far reaching changes since early 1990’s following the phased transition from a pegged exchange rate regime to market determined exchange rate regime in 1993 and subsequent adoption of current account convertibility in 1994 and substantial liberalization of capital account transactions.
Market participants have been provided with greater flexibility to undertake forex operations and manage risk. This has been facilitated through procedural simplification and new instruments,thus leading to hassle free current account transactions for exporters and importers.
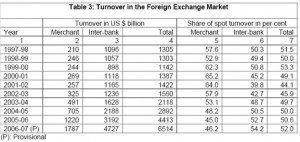
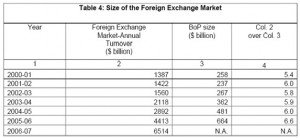
Significant improvements in market infrastructure in terms of trading platform and settlement mechanisms has resulted in liquidity in foreign exchange market increasing by 5 times between 1997-98 and 2006-07. In relative terms the turnover in forex market was 6.6 times the size of India’s balance of payments during 2005-06 as compared with 5.4 times in 2000-01. With the deepening of the foreign exchange market and increased turnover , income of commercial banks through such transactions increased and profit from forex transactions accounted for more than 20% of total profit of scheduled commercial banks in last 2 years.
This cautious and well calibrated approach followed by India while liberalizing forex market is to safeguard against potential financial instability that could arise due to excessive speculation, learning from the lessons of the East Asian financial crisis. There has been a gradual shift from micromanagement of foreign exchange transactions to micromanagement of foreign exchange flows.
Experience in general , in the 1990’s has highlighted the growing importance of capital flows, besides current account deficits and central bank’s inclination to intervene, in determining the exchange rate movements as against trade flows and economic growth in 1980’s and before. In case of most developing countries,which specialize in labour intensive and low and intermediate technology products, profit margins in competitive markets are thin and vulnerable to exchange fluctuations.
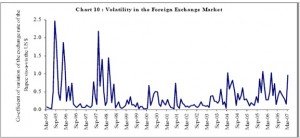
Forex market conditions have remained orderly in the post 1993 period, barring occasional periods of volatility and the approach has been to avoid excessive volatility with lesser intervention of the central bank compared to total turnover.
The exchange rate policy has been guided by careful monitoring and management of exchange rates with flexibility,without a fixed target or pre announced target band and intervention when necessary.
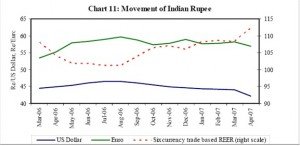
The rupee exhibited two way movements during 2006-07 moving in a range of Rs 43.14- Rs 46.97 per US dollar ,initially depreciating against the USD during the year,reaching Rs 46.97 on July 16 ,2006 reflecting higher crude oil prices, FII outflows and geo-political risks in the Middle-East region. The rupee thereafter strengthened on moderation of crude prices, FII inflows and weakness of the USD in international markets to touch Rs 40.59 per USD on May 7,2007 due to increased supply of dollars in the market. Thereafter the rupee depreciated to Rs 40.85 per USD on May 16,2007. At this level the ruppe appreciated by 6.7 % over end March 2007 and 9.2 % over end March 2006. Against the Euro the rupee appreciated 4.7 % over end March 2007,but depreciated 2.4% over end March 2006. The real effective exchange rate ( REER) of the Indian rupee ( six currency trade based weights) at 112.2 on April 18,2007 appreciated by 12.2% over the base 1993-94 and 9.6% over 2000-01.
Apart from the spot market, the forex market trades in derivates such as forwards,swaps and options. The typical forward contract is one, three or six months. Longer periods are uncommon because of the uncertainties involved. Foreign exchange swaps account for the largest share of the total derivates turnover in India,followed by forwards and options. With restrictions on issue of foreign exchange swaps and options by corporates in India,turnover in these segments essentially reflects inter-bank transactions.

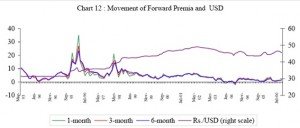
With greater opening of the capital account,the forward premia is getting gradually aligned with the interest rate differential,reflecting growing market efficiency. Though post liberalization the forward premia of the Indian rupee vis-à-vis dollar has generally remained high indicating the rupee was at a discount to the dollar. However in recent times due to enhanced capital flows, build up of foreign exchange reserves beyong the USD 200 billion and growing confidence in the structural reforms of the economy, forward premia has come down sharply from the peaks reached in 1995-96 as shown in chart below.
A recent phenomenon due to the appreciation of the Indian rupee vis-à-vis the USD has been the demand for rupee denominated assets in the international market,including in the developed mature markets.
On June 7, 2007 the Dubai Gold and Commodities exchange has launched the first ever rupee-dollar futures contracts, thus allowing individuals and companies to hedge and trade their rupee risk.
The US based Inter-American Development Bank ( IADB) raised rupee-denominated debt worth Rs 1.5 billion money in the Japanese market in May,2007 ,with payment to be settled in dollars since the rupee is not fully convertible. This shows the expectation of the rupee appreciating and investors wanting to have India in their portfolio and hence the global demand of rupee denominated assets will continue to strengthen on the back of a strong economic growth.
(Concluding part of this article will be posted in the following part)
You might like reading:

Decoding Treasury Inflation Protected Securities – Are they effective?
Inflation has always been a worry and threat to every long-term investors. Any investment which is inflation-protected can protect investors from the loss of purchasing power that inflation can cause. In 1997, US first issued inflation-protected securities called Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities, or TIPS. TIPS are sometimes also known as Treasury Inflation-Indexed Securities. Credit risk and nominal interest risks are the […]

Anirudh Sainath , TEDxNMIMSBangalore 2014
Anirudh Sainath , better known as “Molee” is a freelance digital artist, who started drawing at the age of 3. He is known for his work on Indian mythology inspired by the ancient Indian scriptures. Depicting his artworks online he tries to educate the masses about the narrative aspect of Indian mythology which he feels is ignored today by most […]