Introduction
India is land of spices and produces almost all the spices used in the world. It is the largest producer, consumer and exporter of spice and its’ products. From the ancient time itself, India was centre of Attraction for Rome and China. Further Portuguese, Arabs, Chinese and several other country established trade with India mainly for spices. From ancient time to till now, the charm of Indian spices is still maintained. At present Indian spice industry is as large as it acquires 40-50 percent of the global export volume and 25 per cent in terms of value. The quantity of spices India exports has gone over 4 lakhs tons annually.
Trend in production of Spices in India
The major spices produced in India are chilli, pepper, cardamom (small and large), turmeric, ginger, coriander, cumin, fenugreek, garlic etc. These spices are also the major item of export from India. Most of these spices are being produced in southern state of India. For example Kerala produces around 96 percent of pepper produced in the country.
Table 1: Production trend of spices during last 5 years
|
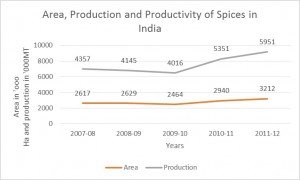
Area, Production and Productivity of Spices in India
(2007-08 to 2011-2012)
|
|
Year
|
Area
( ‘ 000 Ha)
|
Production
( ‘ 000 MT)
|
Productivity
(MT/Ha)
|
|
2007-08
|
2617
|
4357
|
1.7
|
|
2008-09
|
2629
|
4145
|
1.6
|
|
2009-10
|
2464
|
4016
|
1.6
|
|
2010-11
|
2940
|
5351
|
1.8
|
|
2011-12
|
3212
|
5951
|
–
|
Source: Ministry of Agriculture, Govt. of India. (ON255) & (14447)
Spices like cardamom, vanilla, turmeric, ginger, nutmeg, cinnamon, all spice, clove, curry leaf, tamarind, chilli etc. are being produced in Kerala. In India almost all the spices used in the world are being produced. India produces more than 75 spices.
Between 2007-08 and 2011-12, there is a growth of around 23 percent in the area under spice cultivation. Same is the case of production, as during 2007-08 to 2011-12, it has increased by around 37 percent.
Processing of Spices
Spices produced in India are being used as both whole and processed. The spices used for export purpose need to be processed. For example; black pepper exported from India to European country is being processed in the form of Green pepper, White pepper, oleoresin and more than 20 other products. Some of the spices need to be processed as their different part it is used as a separate spice (e.g. Nutmeg). To export spices, maintenance of quality of spice is important. Grading, sorting and standardization of spices are being done to achieve better export revenue.
Import of Spices
Even though India is one among the largest producer of almost all the spices, but India imports spices too. In case of Black pepper, it is the major item of export among the spices, and India imports it too. This is because India is not only the largest producer but also largest consumer of spices. The black pepper produced in India is considered as premium quality pepper in the world market. In recent time Vietnam has established itself as one among the largest producer of pepper. The pepper produced in Vietnam is bold and large sized. The productivity of Vietnam pepper is higher than that in India. The importers are using Vietnam pepper for domestic market. It is well known that Vietnam pepper is considered as a cheap pepper and does not stands with the quality of Indian Pepper.
Table 2: Major Spices which are being imported
|
Spice
|
(Quantity in Tonnes and Value in ₹ lakhs)
|
|
Year
|
|
2011-12 (Estimated)
|
2012-13 (Estimated)
|
|
Quantity
|
Value
|
Quantity
|
Value
|
|
Pepper
|
17565
|
53340
|
15600
|
56944
|
|
Clove
|
12176
|
44081
|
10105
|
45188
|
|
Poppy Seed
|
24075
|
26848
|
11630
|
23221
|
|
Cardamom (Large)
|
2330
|
10390
|
3896
|
14559
|
|
Cassia
|
15655
|
9169
|
12180
|
8226
|
|
Total
|
111136
|
209448
|
131722
|
210232
|
Source: Spices Board India
From the above table it is clear that Import of spices in India is being increasing every year. The major imported spices are pepper, clove, poppy seed, large cardamom, cassia etc. Compared to 2011-12, in 2012-13, the import of major spices has reduced.
In India spices are marketed through different channels. For example, turmeric is being marketed through three basic channel viz. commission agents, regulated market and through marketing co-operative society. In case of village level, even farmers are involved in direct selling of turmeric. If we take example of pepper, we have more than 20 products of pepper and each are being marketed through different channels. Most of the Indian spices are being consumed domestically. Only around 8-10 percent of spices are being exported.
Table 3: Major Spices which are being Exported
|
Spice
|
Quantity in Tonnes and Value in ₹lakhs
|
|
Year
|
|
2011-12 (Estimated)
|
2012-13 (Estimated)
|
|
Quantity
|
Value
|
Quantity
|
Value
|
|
Chilli
|
241000
|
214408
|
281000
|
226144
|
|
Mint Products
|
14750
|
222372
|
19980
|
332179
|
|
Pepper
|
26700
|
87813
|
16000
|
67256
|
|
Turmeric
|
79500
|
73434
|
80050
|
53985
|
|
Cumin
|
45500
|
64442
|
79900
|
109317
|
|
Cardamom
|
4650
|
36322
|
2250
|
18505
|
|
Nutmeg & Mace
|
3620
|
24097
|
3645
|
26095
|
|
Ginger
|
21550
|
20420
|
19850
|
16863
|
|
Total
|
575270
|
978342
|
699170
|
1117116
|
Source: Spices Board India
Data released by Spices Board, India reveals that the export of major spices from India is increasing every year. There is notable increase in both the quantity exported and the value of spices exported. In the year 2011-12 a total of ₹978342 lakh was generated through the export of spices form India. In all the years, the major contributor to the export earnings of spices, pepper and chilli accounts for major chunk. Most of the spices exported are standardized. Spices Board India plays an important role as a bridge between the exporter and the world market and also as a bridge between importer and world market.
New Trend in Spice Trade
Future trading in agricultural commodities has its own history in India. However future trade started in initial period (during 1800’s and 1900’s) was mainly based on single commodity. Due to several recommendations of different committees (Khusro Committee, Kabra Committee, Shrof Committee, Dantwala Committee and The Guru Committee) National Multi Commodity Exchange (NMCE) became the first exchange with permanent recognition by Government to start future trading on 26th Nov, 2002. Further National Commodity and Derivatives Exchange Limited (NCDEX), Indian Commodity Exchange (ICEX) and Ace Commodity Exchange (ACE) started functioning and operating in future market of spices. At present Chilli, Pepper, Cardamom, Cumin, Clove, turmeric, ginger and almost all the spices are being traded in future market. There is a positive growth in future market of spices and people are investing in the future market of spice without hesitation.
Conclusion
India still has maintained the charm of its spices. Trend in production of spices in India gives a positive signal as area, production and productivity of spices are increasing every year. Due to high demand from European country and rest of the world, the export of Indian spices is also showing a positive trend. The new marketing initiative such as future trading in spices has also proven a remarkable success in spice marketing. With these entire positive aspects one can conclude that the future of Indian spices is very bright and the unit/firms involved in production, processing and trading of spices (raw/processed) will gain a better growth.
[The article has been written by Enamul Haque & Anu Peter V. They have completed their PGDABM in NIAM, Jaipur.]