Globally, the solar power industry has been growing rapidly in recent years. In 2010, an estimated total capacity of 17,000 MW was installed globally. Solar radiation over India is 5000trillion KWH/year; in most parts of India, clear sunny weather is experienced 250 to 300 days a year. The country receives more than 4kWh/m2 /day. Major states put together then 979.4MWp is the total amount of energy derived in form of solar. Thus this puts India amongst the highest solar radiation receiving countries of the world.
Favorable policy support from the government is making India a hot-spot for solar generation. Government regulates the solar market through MNRE (Ministry of Renewable Energy) and financial assistance is provided by IREDA (Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency Limited.
Solar power from SPV (Solar Photo Voltaic) system and solar concentrating system is produced in environmental friendly manner, does not generate any waste or pollution, and meets the energy requirement in domestic sector in decentralized manner quite efficiently.
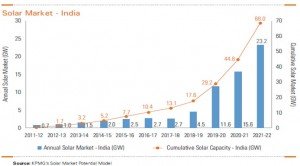
The exhibit below captures their estimates about solar market in India; which shows that there is a steady growth in the solar market after 2017-18.
Key Drivers:
– Cost reduction is achievement of economies of scale,
– Technological advancements
– Emergence of low cost manufacturing locations.
The key driver of the growth of this sector is the concept of Grid Parity. This refers to the point when the cost of the solar power equals the cost of conventional power. In the exhibit below, it shows a band representing solar rooftop costs. The band variation signifies the margins, i.e. the difference between cost and price (includes margins across the value chain). It is expected that the solar tariff to lie anywhere within this band depending on the bargaining power of the developers. And India will reach its grid parity by 2019-20.
Consumer categories:
-Domestic
-Agricultural
Solar powered equipment is more environmentally friendly and economical in its operation compared to equipments powered by an internal combustion engine (ICE) or nuclear power. For irrigation and drinking water solar PV water pumping systems are used in India. Solar water pumping system works on power generated using solar photovoltaic system. The solar energy is converted in to electricity by using a photo voltaic array.
The residential consumer category contributes to about 29 percent of the total Indian Power requirement; this is expected to increase to 34 percent by 2021-22, according to KPMG report. It is expected that high-end residential consumers will be proactive in adopting solar rooftop given their higher power tariffs. A large number of these consumers are likely to start adopting solar power from 2017-18. However, government involvement will be required in encouraging non-high-end residential and agriculture consumers to use solar power.
Solar Market Segment:
-Grid Connected Solar Potential
-Off-Grid Connected Solar Application Potential
-Solar Water Heater (SWH)
Grid Connected Solar Potential includes; Residential Rooftops and Utility Scale Solar power (CSP and PV). And Off-grid connected Solar Application Potential includes; Solar Powered Agricultural Pumpsets and Solar powered Telecom towers.
In the off-grid space, solar power is already cost competitive with alternatives in certain applications. For example, telecom towers are an attractive market for solar PV installations. And Solar Water Heating (SWH) applications could be used in residential, commercial as well as industrial sectors
The whole industry can be analyzed using:
-PEST Analysis and
-Poter’s Five Force Model
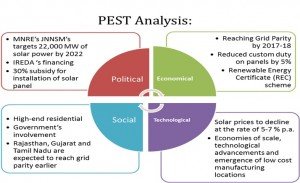
The industry can be analyzed into the following four categories using PEST analysis; which is Political, Economical, Social and Technological.
Political:
The government has huge presence in the Solar Energy market. It regulates the market through MNRE (Ministry of Renewable Energy) and financial assistance is provided by IREDA (Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency Limited). One of the eight missions under the NAPCC is the Jawarlal Nehru National Solar Mission (JNNSM) which was launched in late 2009. The mission targets 22,000 MW of solar power generation.
There are two major financing mechanisms provided by government, i.e.
Equity: Private Equity and Venture Capital.
General eligibility criteria for Solar energy loans:
Applicants:
-Public, Private Limited Companies, NBFCs and registered societies.
-Individuals, Proprietary and Partnership firms ( with applicable conditions)
-State Electricity Boards and eligible to borrow loans from Power Finance Corporation(PFC) or Rural Electrification Corporation (REC)
-Government also provides 30% subsidy for installation of Solar Panel at home.
Economical:
In the recent round of reverse auctioning process for the solar projects under the National Solar Mission, the price discovery for levelized tariff was in the range of INR 10.49/kWh to INR 12.24/kWh for solar-thermal and between INR 10.59/ kWh to INR 12.76/ kWh for solar PV projects.
The budgets has also encouraged private solar companies by reducing customs duty on solar panels by 5% and exempting excise duty on solar photovoltaic panels. The government has initiated a Renewable Energy Certificate (REC) scheme, which is designed to drive investment in low-carbon energy projects.
Social:
According to the KPMG report, the grid parity for the consumer category- domestic and agriculture in 2019-20, based on specific and end-use specific cost economics, the adoption for solar is likely to happen earlier. Certain states will reach this point earlier. For example, the states of Rajasthan, Gujarat and Tamil Nadu are expected to reach this point earlier not only because they have higher solar insulation.
Technological:
It is expected that the solar prices to decline at the rate of 5-7 percent per annum over the next decade, this is because; globally the prices of Solar PV systems have dropped significantly
The solar technology has oligopoly characteristics dominated by a small number of players.
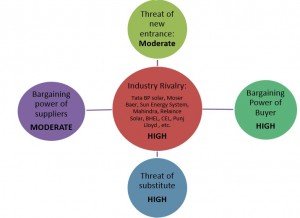
The Solar market can be best explained with the Michael Porter’s Five Force Model, which can be explained with the following diagram:
Suppliers Power:
Solar technology has oligopoly characteristics dominated by a small number of players, but then with government intervention and rising awareness the price of solar energy is coming down. The time taken to reach grid party would also depend on the bargaining power of the developers. Degree of influence exerted over the industry by the suppliers:
-Product is unique and scarce,
-Suppliers are more concentrated in the European market because of better technology.
-High switching costs for the firm in the industry is high.
The Suppliers of the solar energy supplies also too many industries; like rural, agriculture, hospitals, hotels, etc.
There is no substitute product for solar.
The product is critical for the company.
Buyers Power:
The industry’s major power lies within the buyers’ side. Since the awareness in the market is very low, only a small part of residential segment i.e. high end residential consumers is the pro-active group. But for the non-high end residential consumers’ government’s role will be important. Degree of influence exerted over the industry by the buyers:
-Forcing down the prices, since the consumers are price sensitive
-Consumers are demanding in terms of value-added, higher quality
-Low switching costs for the buyers
-Substitute products are available
Threat of new entrance:
The threat of new entrance is not that prominent now but it will be high as soon as grid parity is reached. Since the solar prices are coming down and the support from the government will be the major driver in this regard. Now the segment has high entry barrier but not very low exit barrier so the segment is attractive. The exit barrier is expected to go down after the grid parity is reached. Degree of influence exerted over the industry by the threat of new entrance, are:
-Low scale of economies before the grid parity.
-The technology is not protected.
-Product is not differentiated.
-Government policy makes the entry barrier lower but after the grid parity it is expected to go down.
-The major barrier to entry is the distribution channel.
Threat of substitute product: Another prominent power in the industry is the threat of substitute. The substitute i.e. conventional sources of energy are already present in the market and it is dominated by them. Degree of influence exerted over the industry by the threat of substitute product, are:
-There are many substitute products available
-Customers’ switching cost is low as they can easily switch over to them as there price is less.
Industry Rivalry: The intensity of rivalry from the direct competition i.e. companies dealing in solar equipment, is low but from the indirect competition i.e. companies dealing in conventional residential pump it is very high. Degree of influence exerted over the industry by the industry rivalry, are:
-Market is crowded with indirect competition from indirect competition but with some direct competition.
-Switching cost for the consumers for the conventional market is low.
-Some prominent companies in the solar market, whose brand image is much higher, like Tata, Relaince, Mahindra, BHEL, Moser Baer, etc.
Solar power has tremendous potential to meet almost 7 percent of our power needs by 2022, mitigate 2.6 percent of our carbon emissions in that year and save over 71 MTPA of imported coal in that year (equal to USD 5.5 bn of imports). The imperative for action today is strong and therefore is the case for persistence and consistency on part of the Government. For the industry, this represents a significant investment opportunity. Investment opportunities across the value chain from manufacturing to EPC to project development over the next decade.